Database
Data interoperability
Data interoperability refers to the ability of different data systems, applications, and technologies to exchange, interpret, and use data in a seamless and efficient manner. It ensures that information can be transferred and utilized between different systems, platforms, or organizations without loss of meaning, integrity, or functionality. Data interoperability is not just about moving data from one system to another—it also requires that the receiving system understands the data in the same way as the sending system, enabling meaningful use of the information.
Data interoperability is critical in modern organizations and technological environments, where multiple systems, software applications, and databases are used simultaneously. It plays a foundational role in data-driven decision-making, efficient operations, collaboration across organizational boundaries, and the development of innovative technologies.
Importance of Data Interoperability
Data interoperability is important for a number of reasons, as it directly impacts collaboration, efficiency, integration, and innovation:
Collaboration: Data interoperability allows for effective collaboration between organizations and individuals by enabling seamless data sharing. For example, healthcare organizations can share patient data securely and accurately between hospitals, laboratories, and insurance providers, improving patient care and reducing duplicate tests.
Efficiency: By allowing different systems to exchange and process data efficiently, organizations can save time, reduce operational costs, and minimize errors. For example, financial institutions can process transactions faster when customer and account data is interoperable across systems.
Integration: Interoperable data enables different software systems and technologies to integrate smoothly, forming a cohesive and comprehensive data ecosystem. This integration supports real-time analytics, reporting, and operational automation.
Innovation: By ensuring that data can be used across multiple platforms, interoperability fosters innovation. Developers and organizations can build new applications, predictive models, or AI systems on top of existing datasets without being hindered by incompatible data formats or structures.
In today’s increasingly data-driven environment, organizations that fail to achieve data interoperability may face inefficiencies, data silos, and increased costs, which can negatively impact their competitiveness and innovation potential.
Standards and Technologies Supporting Data Interoperability
Data interoperability is supported by a variety of standards, protocols, and technologies designed to enable seamless data exchange and understanding:
XML: Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a widely used format for structuring and exchanging data. It provides a flexible way to describe and transport information between different systems.
JSON: JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) is a lightweight data-interchange format commonly used for transmitting data between web applications and APIs. JSON is human-readable and easy for machines to parse.
REST: Representational State Transfer (REST) is an architectural style for building web services and APIs that allows systems to communicate over HTTP using standard methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE.
OGC: The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) develops standards for geospatial data interoperability, enabling geographic data to be shared across mapping, GIS, and remote sensing systems.
HL7: Health Level Seven (HL7) develops standards for exchanging healthcare data between systems, ensuring that patient information can be shared across hospitals, labs, and clinics accurately and securely.
By adhering to these standards, organizations can achieve consistent, reliable, and meaningful data exchange that is compatible across different platforms and applications.
Data Standardization
Data standardization is the process of defining and implementing a set of rules, formats, and protocols to ensure that data is consistent, accurate, and compatible across different systems, applications, and organizations. Without standardization, even interoperable systems may encounter issues due to inconsistent formats, terminology, or structures.
Key aspects of data standardization include:
Data Modeling: Creating a common structure or schema for data, specifying the types of data elements, relationships between elements, and constraints.
Data Formats: Establishing standardized formats for representing data, such as XML, JSON, or CSV, ensuring compatibility across systems.
Terminology: Developing a common vocabulary to describe data, reducing misunderstandings and inconsistencies when sharing information across organizations.
Data Exchange Protocols: Defining rules and methods for data transfer, such as REST, SOAP, or secure FTP, to facilitate reliable and secure communication between systems.
The benefits of data standardization include:
Improved Data Quality: Standardized rules reduce errors, inconsistencies, and missing data, improving overall data quality.
Increased Efficiency: Standardized formats and protocols streamline data exchange and processing, saving time and resources.
Interoperability: Standardization makes it easier for different systems to exchange and use data effectively.
Improved Governance: Organizations can manage data consistently, ensuring compliance with legal, regulatory, and security requirements.
Standardization forms the foundation for true interoperability, enabling data to be shared reliably and used meaningfully across diverse systems.
Data Interoperability and Licensing
Data interoperability and licensing are closely linked, especially when sharing or reusing data. Licensing defines the legal terms under which data can be accessed, used, and redistributed, and it is essential to consider these terms when designing interoperable systems.
Data Interoperability
- Allows different systems to exchange and interpret data efficiently.
- Facilitates collaboration across organizations, departments, and platforms.
- Requires careful attention to data mapping, transformation, and standardization to ensure consistency and usability.
Licensing
- Defines the legal rights and restrictions associated with data use.
- Protects the data owner while enabling others to use data for research, analysis, or commercial purposes.
- May require attribution, prohibit commercial use, or limit redistribution depending on the license type.
When sharing data, organizations must ensure that their interoperability solutions comply with licensing terms. For instance, if a public agency shares data under a specific open data license, downstream systems must respect these usage restrictions while still enabling interoperability.
REST Principles
REST (Representational State Transfer) is a common architectural style used for building interoperable web services. RESTful APIs follow a set of principles that ensure scalability, maintainability, and simplicity:
- Client-Server Architecture: Separates client and server responsibilities, allowing independent scaling and development.
- Stateless: Each request contains all information needed to complete it, eliminating server-side session dependencies.
- Cacheability: Responses can be cached to reduce redundant requests and improve performance.
- Uniform Interface: Standardizes the API design to simplify interaction and ensure consistency across resources.
- Layered System: Supports multiple intermediary layers for security, scalability, or processing without impacting the client-server interaction.
- Code on Demand (optional): Allows servers to transmit code to clients to execute specific functions.
REST principles enable systems to communicate efficiently and flexibly, forming a key component of modern data interoperability strategies.
Data Interoperability vs Open Data
While related, data interoperability and open data are distinct concepts:
- Data Interoperability: Focuses on enabling different systems to exchange and use data effectively, even across diverse formats and platforms.
- Open Data: Refers to publicly available data that anyone can access, use, and reuse, often in standardized formats to facilitate transparency, research, and application development.
In practice, combining open data with interoperability standards allows organizations and individuals to leverage publicly available datasets across multiple platforms and applications effectively.
Tracker Ten and Data Interoperability
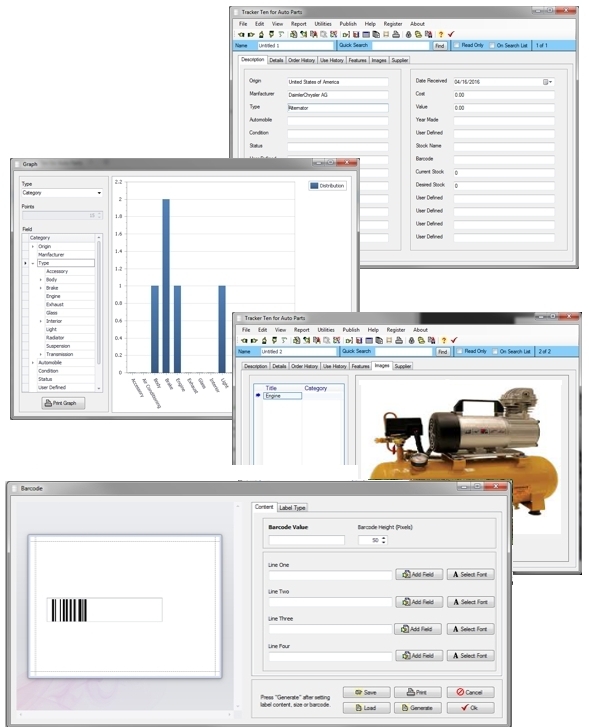
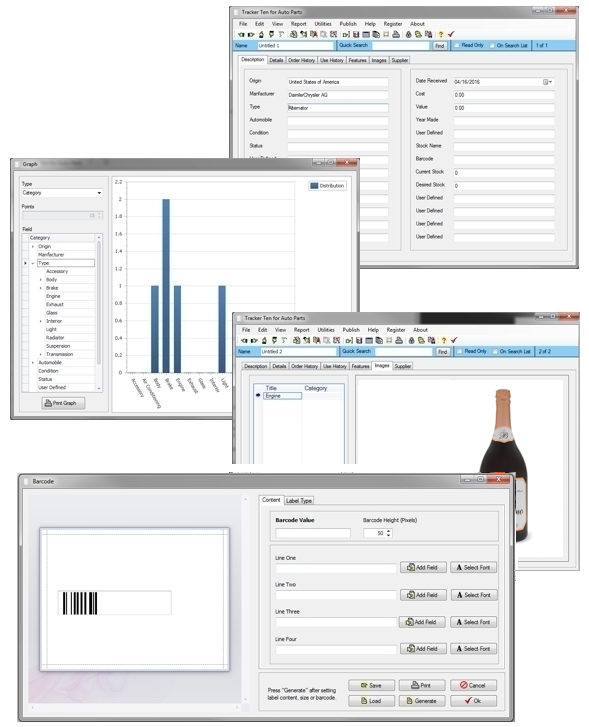
The Tracker Ten software suite is designed with interoperability in mind. Tracker Ten supports import and export to comma-separated values (CSV) format, which is compatible with nearly all database systems, spreadsheets, and analytical tools. This ensures that data managed in Tracker Ten can be seamlessly shared with other systems, enhancing collaboration, reporting, and integration. Users can combine data from multiple sources, transform it as needed, and use it in various applications without compatibility issues.
By supporting standardized formats and providing flexible export/import options, Tracker Ten empowers organizations and individuals to maintain efficient, interoperable workflows while complying with licensing and usage restrictions. This allows small businesses, educational institutions, and larger organizations to maximize the value of their data and integrate it effectively with other systems.
Overall, achieving robust data interoperability requires a combination of standardized formats, adherence to protocols like REST, careful consideration of licensing terms, and the use of tools like Tracker Ten that facilitate seamless data exchange. When implemented correctly, data interoperability improves efficiency, supports innovation, enables collaboration, and ensures that data remains a strategic asset for organizations of all sizes.
Looking for windows database software? Try Tracker Ten
- PREVIOUS Invoicing and Tracking Software for Contractors Saturday, April 1, 2023
- NextSpeeding Up Data Entry Thursday, February 2, 2023